Scientist Profile

Dr.(Smt.) Sujata Kalyan Mandke
Designation
: Scientist D
Phone
: +91-(0)20-25904508
Fax
: +91-(0)20-25865142
Email ID
: amin[at]tropmet[dot]res[dot]in
| Degree | University | Year | Stream |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ph.D | Pune University | 2010 | Physics |
| M.Tech. | Pune University | 1992 | Atmospheric Science |
| M.Sc. | Nagpur University | 1990 | Physics |
| B.Sc. | Nagpur University | 1988 | Physics, Mathematics, Electronics |
 Indian summer monsoon variability with focus on intra-seasonal variability
Indian summer monsoon variability with focus on intra-seasonal variability
 Tropical cyclones over North Indian Ocean
Tropical cyclones over North Indian Ocean
 Polar-Indian summer monsoon Teleconnection
Polar-Indian summer monsoon Teleconnection
| Award Name | Awarded By | Awarded For | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third rank | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune | Third rank in Research Oriented Training Programme 1992-93 in Meteorology, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune. | 1992 |
| Year | Designation | Institute |
|---|---|---|
| 2011-Present | Scientist D | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2003-2010 | Scientist C | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1999-2003 | Scientist B | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1994-1999 | Junior Scientific Officer | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1993-1994 | Research fellow | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1992-1993 | Research fellow | Centre for Mathematical Modelling and Computer simulation, Bangalore |
Research Highlight
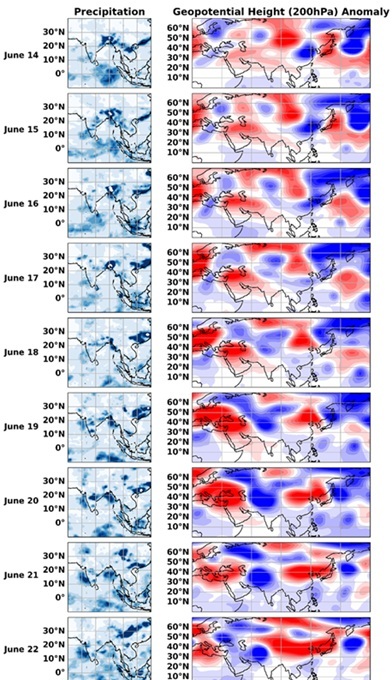
Mandke Sujata K. and Vaisakh, S.B. Towards Understanding the weekly rainfall variability over India in June 2022, Climate Dynamics (online), 63:154, March 2025
This study investigates the factors driving distinct weekly rainfall variability over India during June 2022 and identifies the mechanisms that led to the large excess rainfall over northwest India in its third week using multiple observed datasets. The rainfall over India in June 2022 was characterized by pronounced variability on weekly scale, along with the uneven spatial distribution from week to week. The country experienced the deficient rainfall in the first (-42%) and second (-24%) week, followed by excess rainfall (+ 44%) in the third week and again deficient rainfall (-30%) in the fourth week of June 2022. This weekly rainfall variation is found to be influenced by: (i) anomalous large-scale circulation modified by the intensity and location of Western Pacific subtropical high (ii)subtropical upper tropospheric Asian jet over north India. This study further analyses the large excess rainfall over northwest India in the third week of June 2022. The background active phase of Indian monsoon and the southward penetrated upper tropospheric midlatitude trough of Rossby wave located over northwest India, interacted with each other, and reinforced the prevailing active monsoon condition over the region. This facilitated the excess rainfall over northwest India.


